Ever wonder how Enterprise Access, Star, Ingres, Ingres Net, OpenROAD, and all the other offerings fit together?
Do you need to understand which drivers to use, how to interface and take advantage of Ingres within your solution?
This document is written based on a VIP presentation given by Bruce Lunsford, Architect, Ingres Engineering and gives an overview of how the various products work together and how to adapt the Ingres family of solutions to meet your needs:
-
Ingres Architecture Overview
-
Ingres/Net & GCF
-
Application Environments
-
Enterprise Access
-
EDBC
-
STAR
-
Replicator
-
OpenROAD Application Server
4. Enterprise Access (EA)
Ingres Enterprise Access is designed to provide a consistent relational interface to a number of different datasources residing on various platforms.
-
Commonly referred to as a “Gateway”
-
From OpenROAD or Ingres Client to a non-Ingres DBMS
-
Client generally unaware that DBMS is not Ingres
-
Where you see “Ingres DBMS”, substitute “EA”

NOTE that EA looks like an Ingres database to the various applications. EA just “plugs in” where an Ingres DBMS would normally be. Additionally, they can coexist in the same installation so that the application can access Ingres through one connection and can access non-Ingres databases through another connection.
SQL Access to Datasources
Through Enterprise Access, data is accessed via SQL regardless of the datasource type (Relational or Non-Relational datasources).
The SQL access requires the following:
-
Consistent SQL dialect implementation
-
Consistent metadata interface
-
Consistent messaging interface (GCF)
Consistent SQL Dialect
Applications are portable across Ingres and non-Ingres via EA if they stick to using OpenSQL. That is, without even recompiling, the application can run “as is” against any EA database… only the connection string changes. OpenSQL is:
-
Implemented in all Ingres clients and servers
-
Based on SQL92 entry with Ingres specific extensions
-
Part of native Ingres SQL dialect
Applications are not limited to using just OpenSQL; most of the target databases support more than just OpenSQL. However, if the applications use non-OpenSQL statements, they are not guaranteed to run correctly against the other EA databases.
Relational Datasource Support
-
The Gateway acts as an intermediary by performing the following functions
-
Translates OpenSQL queries to native DBMS dialect
-
Transforms OpenSQL data types to native DBMS data types
-
Handles OpenSQL metadata queries
-
Physically interfaces to native datasources
-
Handles responses and results from native DBMS
The Enterprise Access allows seamless access to a wide variety of relational and non-relational data stores
-
Enterprise Access
-
SQL Server
-
Oracle
-
DB2UDB
-
RMS
All data stores look like Ingres databases. They are accessed through SQL embedded directly in the OpenROAD 4GL and/or accessed via ODBC, JDBC or .NET Data Provider.
While access to non-Ingres databases is supported through ODBC, JDBC and .Net, it is somewhat uncommon because applications will tend to use the native non-Ingres drivers in those situations. However, a benefit of using EA is that the application only requires one driver (the Ingres one) to access any database supported by EA.
Enterprise Access Benefits
-
Real-Time Access, no extracts
-
One Copy of Data for Everyone
-
Access from any platform or client
-
Supports distributed database processing
-
Supports replication
Enterprise Access Uses
-
Migration from other DBMS’s to Ingres
Use EA to copy data from non-Ingres databases to Ingres. Can also test new or modified applications with the non-Ingres data and compare when run against Ingres.
-
Introduce Ingres into new environments
Build new projects using Ingres and access existing data in other databases “as needed” via EA. In that way, existing non-Ingres applications and data are not disrupted or affected by the new Ingres application. Data that already exists in other databases doesn’t need to be duplicated in Ingres.
-
Applications written for Ingres run against any DBMS
Many ISVs that have written their applications in OpenROAD are able to sell their software to customers and run the software using the database that the customer already has in place or prefers. The ISVs then don’t need to have special versions of their software for different databases.
-
Federated Data Store
EA links applications to Ingres and other databases through one common interface and dialect of SQL.
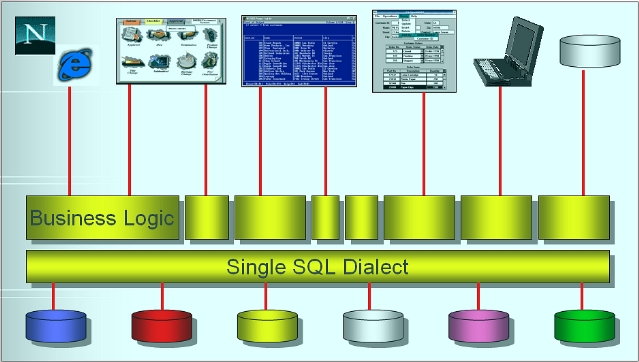
One common view of all data sources, with business objects defined to satisfy your existing and future business rules. Now you have achieved database independence.
5. EDBC (Enterprise Data Base Connectivity or “ODBC/JDBC Everywhere”)
The Corporate Dilemma
-
Legacy data is locked away in mainframes
-
Billions of dollars have been invested in legacy application development
-
Developing new mainframe applications is slow and expensive
-
Corporations need to Web-enable their legacy data and systems
-
Migration of data not an option (legacy apps are still serving business needs)
-
Legacy applications can be difficult to integrate
EDBC is DATA Access Middleware
-
EDBC allows Web-generation application development tools to leverage corporate DATA directly
-
No need for new or pre-existing applications on the host
-
EDBC is non-intrusive: it integrates seamlessly with existing transaction systems (CICS/TS, IDMS/DC, IMS/TM etc)
EDBC Architecture and Functions
-
Same basic architecture as EA
-
OpenSQL support
-
Relational and non-relational gateways
-
Mainframe based
-
Makes mainframe DBMS’s look like Ingres to the applications
-
Separate EDBC client provided
-
Can use Ingres client instead
-
EDBC often used standalone
-
Extends Ingres reach to mainframe DBMS’s
EDBC does not require any Ingres components and is often installed and deployed independently of Ingres, primarily to provide ODBC and JDBC access to the mainframe. On the other hand, EDBC is fully interoperable with Ingres and fits well into a federated data scheme.
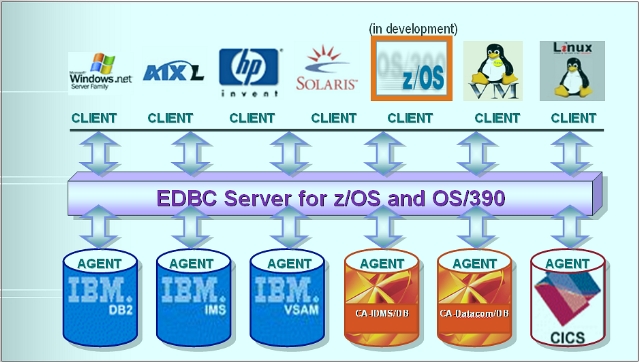
|
Clients |
Windows, Linux, AIX, Solaris, HP/UX and Linux/390 |
|
Server |
z/OS and OS/390 |
|
Agents |
DB2, VSAM, IMS, IDMS, Datacom and CICS/VSAM |
EDBC Client Components
-
Platforms
-
Windows: XP, 2000, 2003
-
UNIX: AIX, Solaris, HP/UX, Linux
-
Mainframe: Linux/390 and z/OS
-
Subset of Ingres Client components
-
No Forms-based Development tools (ABF, QBF, RBF, etc)
-
ODBC and JDBC (*focus*)
-
Network configuration utility
-
Database Object Manager (Visual DBA)
-
COBOL Data Mapping Utility (VSAM and IMS)
-
Interchangeable with Ingres client
-
EDBC client can access Ingres or EA servers
-
Ingres client can access EDBC servers
Ingres, Enterprise Access, EDBC

Any application language and interface can access data stores on Ingres, IMS, Oracle, etc … all done transparently through Ingres, EDBC and/or EA.
6. Architecture with STAR
Now we throw Ingres Star into the picture. What you get is a SINGLE LOGICAL VIEW of your entire data environment… a true Federated Database! Tables are first linked into a Star database by the DBA. Then the application connects to the Star database instead of each of the target databases. All of the tables linked to the Star database look like normal tables to the application and can participate in JOINs and other SQL features that would be difficult to do in the application across tables from different databases.

NOTE that EA and EDBC are just options if needed for access to non-Ingres databases. Star works equally well across multiple Ingres databases. Star supports 2 phase commit across Ingres databases for updates and implements 1 ½ phase commit protocol when any of the databases are non-Ingres.
Federated Database View

This is a VDBA view of an EDBC installation (called “Long Island OS390”) and an EA installation (called “Long Island Solaris”). While not shown here, Ingres installations would also show up similarly. Ingres/Star can be used to consolidate any desired tables into a single logical database view.
7. Ingres, EA, EDBC, STAR, + Replicator
Now to really complicate things, let’s throw Replicator into the picture! Although Replicator is considered a separate component, it is actually implemented in the Ingres DBMS. It allows for bi-directional replication between Ingres databases and 1-directional replication from Ingres databases to non-Ingres databases via EA or EDBC.

8. OpenROAD Overview
OpenROAD is the Ingres GUI application development and runtime product.
-
OpenROAD is a powerful RAD solution that combines:
-
A comprehensive, graphical, component based IDE
-
A highly productive, 4GL based object-oriented modeling, design and programming environment
-
A framework, platform and database agnostic, high-performance client and server runtime infrastructure
-
OpenROAD is used to:
-
Build large scale, n-tier mission critical business applications
-
Deploy robust, rich browser (thin) and desktop (thick) apps
-
Integrate and coordinate a wide variety of architectures (Java, .Net) and enterprise data stores
OpenROAD Components
There are 3 main OpenROAD components:
1) Development Workbench
-
Platform independent
-
Graphical forms development
-
Object-oriented 4GL
-
Interactive debugger
-
Database independence
-
Support for external controls
-
Build fat/thin clients and server components

2) OpenROAD Server (aka the “App Server”)
-
Platform independent
-
High-performance architecture
-
Visual Server Farm Admin
-
Client agnostic access (Java, .Net, VB, ASP, JSP, OpenROAD, etc.)
-
Supports XML In/Out
-
Client access via DCOM or HTTP (through any web server)

3) Thin (browser, mobile) and thick (desktop) client OpenROAD applications
-
Platform independent
-
Rich browser (thin) or desktop (thick) applications
-
Secure application delivery

All components and the end-user applications can run on any of the supported platforms (hence, platform independent).
OpenROAD Platform Support
-
Windows
-
Linux
-
HP-UX
-
Sun Solaris
-
AIX
-
HP Tru64
Ingres Tools Evolution Continues
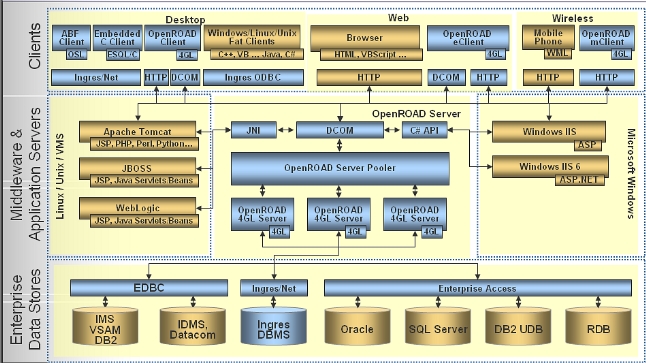
The OpenROAD Server (in the middle of the diagram) communicates via DCOM to applications of many languages and environments. This allows the user to move their OpenROAD 4GL business logic into the OpenROAD Server and be driven from not only desktop and web OpenROAD applications, but also from Java, ASP.Net and virtually all applications in the enterprise. Since OpenROAD Server also operates as an Ingres client, it can access all of the databases supported by the Ingres family of products. You can’t get much more “connected” than that!
Summary
Ingres is an “enterprise” architecture.
-
The architecture supports
-
Any type of Ingres or industry-standard application
-
Accessing any DBMS
-
On any platform
-
Transparently!
-
Ingres is committed to supporting popular application languages via driver technology
-
New drivers automatically get access to all that the Ingres products offer
-
Use STAR to
-
Simplify heterogeneous DBMS environments to the applications & users
-
Join data across DBMS’s (keep the application simple)
-
Migrate data (with EA and EDBC)
-
Replicator
Another tool for data access and migration -
OpenROAD Application Server is not just for OpenROAD apps…



